Entrepreneurship and business operations can be extremely thrilling. It requires considerable effort, but it might be worthwhile in the end. In essence, operating a self-employed business entails using it independently, rarely answering anyone other than clients, and frequently having the flexibility to determine one’s working hours. Profits will increase if you strategically employ your cards and successfully implement an excellent concept.
While money may not be everything, it is undoubtedly a primary concern for individuals embarking on their first ventures in the realm of business. Although you may express your desire to effect positive change in the world to your vendors, investors, and loan officers, they will probably require evidence beyond your good intentions.
What Is A Good Profit Margin?
Before proceeding, we must review the concept of profit margins. The profit margin is a prevalent profitability ratio utilized to assess how organizations generate revenue. The profit margin signifies the overall proportion of income converted into earnings.
Remember that to obtain the profits, you must deduct every expense associated with operating the business. Profit margins indicate to stakeholders (including investors, creditors, and others) how efficiently a company manages its funds.
Types Of Profit Margin
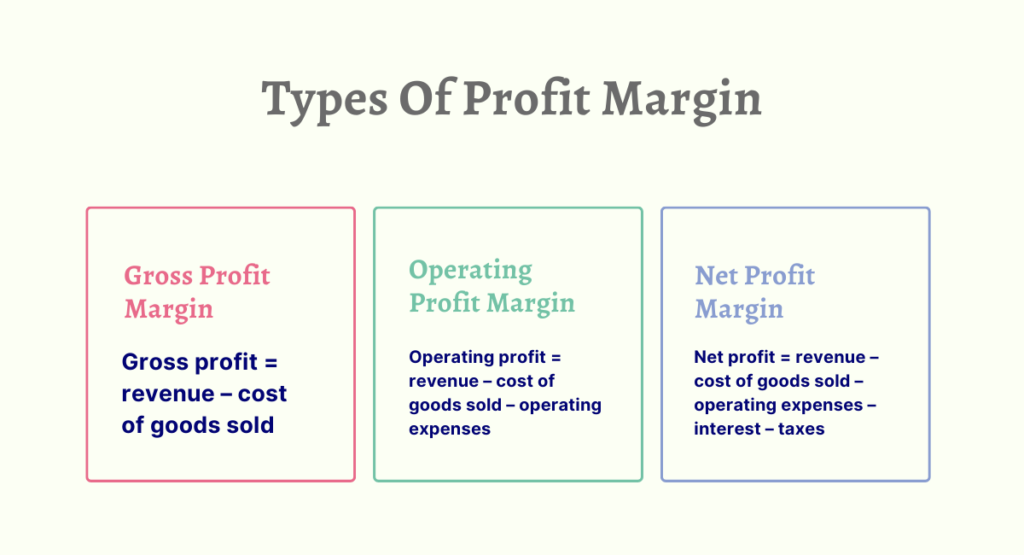
Investors, business proprietors, accountants, creditors, and lenders utilize three distinct categories of profit margins. One can compute their organization’s gross profit margin, operating profit margin, or net profit margin.
Each of these three formulas facilitates the formulation of well-informed business decisions by providing distinct insights into one’s financial well-being. Consult our analysis of each margin for further information.
1. Gross Profit Margin
The gross profit is the remaining revenue after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). The expenses required to produce or manufacture your goods or services are COGS. Raw materials, labor wages, and factory administrative expenses are a few examples.
To calculate gross profit, one may employ the subsequent formula:
- Gross profit = revenue – cost of goods sold
Once the gross profit has been computed, the gross profit margin can be ascertained as follows:
- Gross profit margin = (gross profit ÷ revenue) x 100
Gross profit margin is a more suitable metric for assessing individual items’ profitability than an entire enterprise. Vital operating expenses may cause a company that appears to be in good financial shape and has robust total sales to incur losses. By calculating gross margin, one can determine whether or not a particular product or service requires excessive labor or time.
2. Operating Profit Margin.
Operating profit is the residual revenue after deducting operating expenses (OPEX) and product cost (COGS). COGS is the actual cost incurred in producing your goods or providing your services.
Conversely, operating expenses pertain to the financial outlays required to sustain the operation of a business. This category contains rent, payroll, inventory software, and marketing expenses. Expenses such as taxes and interest payments are not included.
Commence by computing the operating profit:
- Operating profit = revenue – cost of goods sold – operating expenses
Then, the operating profit margin formula can be applied:
- Operating profit margin = (operating profit ÷ revenue) x 100
When seeking a comprehensive assessment, utilizing either the operating profit or net profit margin is advisable.
3. Net Profit Margin
The amount remaining after deducting COGS, OPEX, interest, and taxes is the net profit.
Calculate your net profit by applying the following formula:
- Net profit = revenue – cost of goods sold – operating expenses – interest – taxes
Then, enter the following variables into the formula for net profit margin:
- Net profit margin = (net profit ÷ revenue) x 100
The net profit margin is considered a highly reliable indicator of a company’s profitability due to its inclusion of both significant direct and indirect costs. Hence, net income serves as the conclusive figure on the income statement, detailing the profit and loss of a business during a specified period. It is the most crucial takeaway once expenses and revenues have been deducted.
What Is A Good Profit Margin For A Product?
According to a report by NYU on U.S. margins, the mean net profit margin across industries is 7.71%. However, this does not imply that your optimal profit margin will be precisely this amount.
As a general rule, a healthy margin is 10%, a low margin is 5%, and a large margin is 20%. However, a one-size-fits-all approach to establishing objectives for the profitability of a business is not optimal.
To begin with, certain enterprises are inherently high-margin or low-margin enterprises. Grocery stores and retailers, for example, operate with minimal margins. As their sales increase, they must purchase inventory, hire corporate and labor workers, facilitate transportation and distribution, and rent more extensive facilities, contributing to their high expenses.
However, foodstuffs and certain consumer goods with minimal profit margins are typically more straightforward to sell. A market characterized by intense competition, such as the ongoing rivalry between ridesharing companies Uber and Lyft, may also result in razor-thin profit margins.
In contrast, the gross margins of software-as-a-service (SaaS) and consulting firms are typically relatively high. These enterprises have reduced operational expenses, do not carry inventory, and demand for startup capital is minimal. Businesses that retail expensive items, such as jewelry stores, may also be classified within this category. The most profitable and least profitable industries are discussed in greater detail here.
Expect Differences Between Your Gross, Operating, And Net Margins.
Examining an actual-life instance is an excellent method to demonstrate the distinctions among the margin formulas. Examine the margins of Amazon as of March 2020:
- Margin of gross profit: 26.06%
- Operating profit margin: 5.29%
- Margin of net profit: 3.36%
As each margin represents a marginally more significant portion of the company’s expenditures, profits will likely diminish across different formulas. However, your company may experience a less pronounced decline in gross profit margins than the others.
It is essential to consider that a prosperous multinational corporation like Amazon will incur operating expenses and additional expenditures significantly surpass most startups. As a result, they can anticipate reduced operating and net margins.
Ways To Improve Your Profit Margin
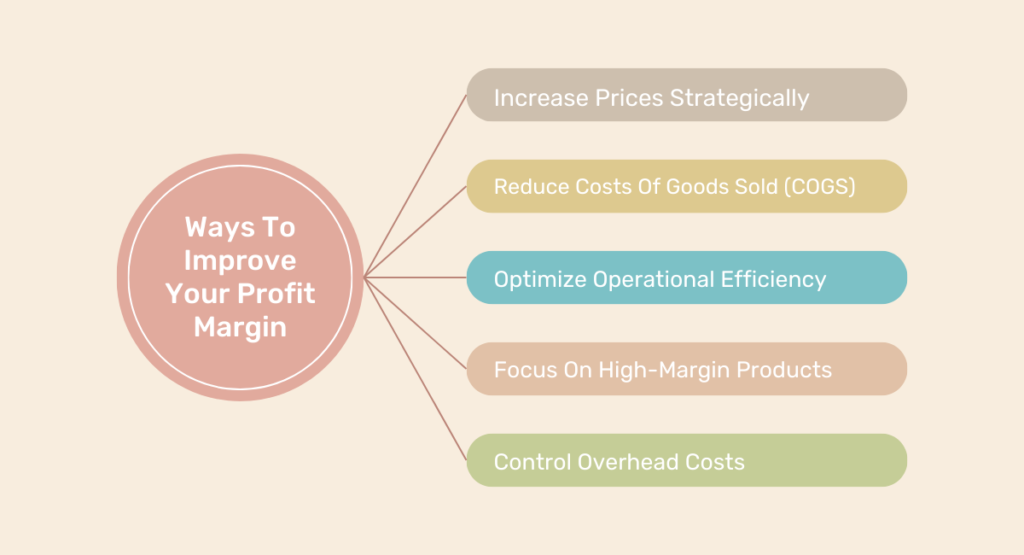
It is critical to increase your profit margin to maintain and expand your company. A more significant profit margin signifies a more lucrative organization that effectively controls its expenses compared to its income. Listed below are several techniques for increasing your profit margins:
1. Increase Prices Strategically:
Verify that your pricing strategy accurately reflects the value you provide, your market position, and your competitors’ pricing. When the value proposition is unambiguous, even modest increments can substantially affect profit margins without resulting in customer attrition.
2. Reduce Costs Of Goods Sold (COGS):
To reduce waste, negotiate more favorable terms with suppliers or locate substitutes offering superior quality or lower prices. Consider long-term contracts or volume purchases to negotiate reduced material costs.
3. Optimize Operational Efficiency:
Streamline operations via automation and process enhancements. Profit margins can be increased and operational expenses reduced by optimizing inventory levels, enhancing productivity, and decreasing waste.
4. Focus On High-Margin Products:
Conduct a profitability analysis of every product and service. Concentrate on increasing the sales of high-margin items while contemplating the gradual elimination of low-margin products or services that make a negligible contribution to overall profitability.
5. Control Overhead Costs:
Review ancillary expenses such as rent, utilities, and administrative costs routinely to identify opportunities for cost reduction. Contract renegotiation or transitioning to more cost-effective providers should be considered.
Profit Margins Of New VS. Established Companies
In general, many newly founded business proprietors anticipate a lower profit margin during the initial years of operation. It is not that they intend to generate diminished profits. They believe that starting a business requires considerable capital, time, and effort; therefore, generating a profit may require some time.
When you earn a respectable profit margin, your amount can vary depending on your industry. However, this is unexpectedly false in other situations. Certain enterprises have a greater propensity for maintaining higher profit margins than others.
Those with lesser profit margins frequently incur more significant overhead and expenditure costs. Entrepreneurs operating within the food service sector are confronted with managing inventory, rent, utilities, and labor. However, their products and services are frequently more straightforward to market.
There is occasionally an inverse correlation between sales and profit margins. For example, profit margins in the manufacturing and service sectors decline as sales volume increases.
These industries may experience a 40% profit margin until they reach approximately $300,000 in annual revenue. At that point, the company will likely be required to employ additional personnel. Each employee reduces the profit margins of a small enterprise.
In Summary, A profit margin for a product is a relative metric contingent upon industry norms, competition, and operational effectiveness; there is no such thing as a “good” profit margin in general. In business, profit margins about the particularities of the market and operational processes must be perpetually evaluated. By comprehending these elements and executing tactics to enhance pricing and diminish expenses, organizations can strive to attain and uphold profit margins that subsidize activities and stimulate expansion and novelty.
Thank you for reading……


