Net income, or net earnings, is the amount of money a company or individual earns after subtracting all the costs and expenses. It shows how much profit or revenue is left over after paying for everything. Investors use this number to see if a company is making more money than it is spending.
Net income is shown on a company’s financial statement and measures how profitable the company is. For individuals, net income is their income after taxes and deductions are removed.
What Is Net Income Loss?
For a business, net loss is when it loses more money than it earns. This can also be called a net operating loss. For tax reasons, if a business has a net loss, it can use that loss to reduce its taxes in future years when it makes a profit. A net loss is shown on the company’s financial statement. It is calculated by subtracting expenses from revenues:
Net Loss (or Net Profit) = Revenues – Expenses
A company makes and spends money at the same time. A net loss is an example of the matching principle. The matching principle is an integral part of the accrual accounting method. Expenses related to money earned in a specific period are recorded in that same period, regardless of when the payments are made.
Components Of Net Income Loss
To better understand what a net loss is and how to determine it, let’s analyze the main parts of the definition we mentioned earlier.
1. Revenues
The word revenue means all the things a company sells to people. On the income statement, revenues make money for the company.
Interpretation
When the company makes more money, it shows it is growing and selling more things. It can then choose to spend more money on investments or expenses. On the other hand, if the company is making less money, it means it is getting smaller. To keep making money, it needs to spend less quickly.
2. Expenses
The expenses in the income statement are the company’s costs for providing services or making goods to sell.
In most cases, there are three macro-categories of expenses.
- The price of items (such as the price of the materials used to make them)
- The business costs (such as wages, rent, bills, loan repayments, etc.)
- The costs of borrowing money (money owed to the shareholders)
Interpretation
For a company to make money, it must spend less than it earns. This means the money it brings in must be enough to cover all its costs and pay its employees. If this doesn’t happen, the company loses money, and the fees are higher than the earnings.
Income Statement
The income statement is a report companies create to show their financial results. It includes all the money the company earned and spent during a specific period.
While the basic structure of an income statement is the same for all companies, some industries may have additional information.
Importance Of Net Income/Net Loss
Net loss or net income is crucial to evaluate a company’s performance in a specific time frame. Investors analyze the size of the net loss or net income and compare it to previous periods to gauge the company’s progress.
How Do You Calculate Net Income Loss?
The income statement shows how much money you made and spent. Ultimately, it tells you if you made a profit or loss. Profit means you made more money than you paid, while loss means you spent more money than you made. The calculation for determining loss is revenue minus expenses equals loss or profit. Here’s its formula:
Net profit/loss = total revenue or income – total expenses
Here’s a step-by-step guide for calculating net loss:
- Determine your total income. Determine the total revenue generated by the business as a preliminary step. Revenue is the initial quantity on a financial statement, assuming net loss and net income are the final figures.
- Locate expenses. Calculate the operating expenses to determine the total cost of the business. This includes the organization’s recurring expenses and variable costs that various factors may influence.
- Subtract the costs from the income. A negative result represents the net loss, which indicates the amount of money the company lost. A positive numerical result signifies the net profit.
Factors That Lead To A Net Loss
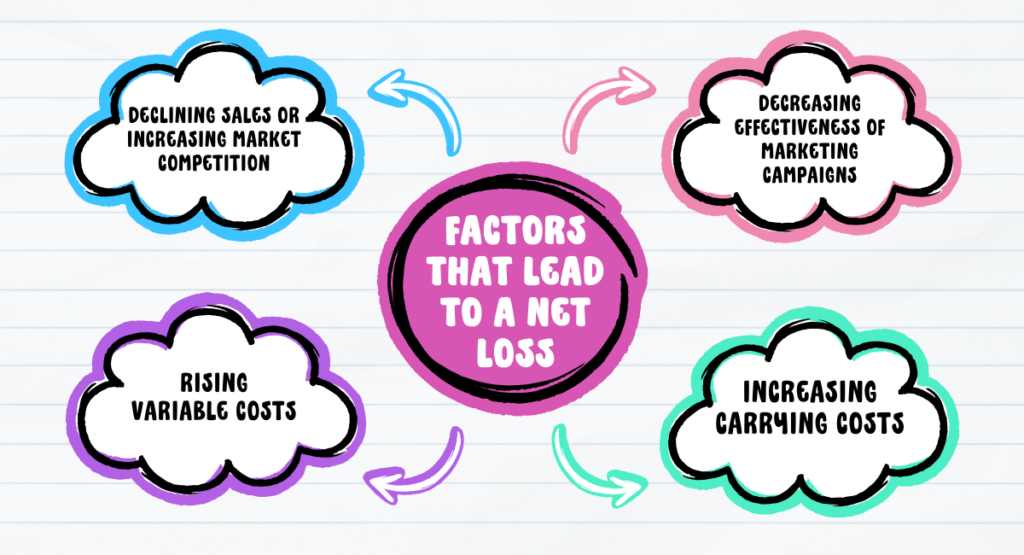
The following factors may contribute to an underachieved revenue for a business, resulting in a total loss:
1. Declining Sales Or Increasing Market Competition
When a competitor captures customers, there is a decline in revenue, which results in a loss. This may occur if customers favor the products of a competitor, if that competitor has superior marketing, or if they offer lower prices.
For example, a new entrant in the industry might present an excellent product or a more affordable service. Customers may subsequently utilize their service or product, decreasing sales and losses.
2. Decreasing Effectiveness Of Marketing Campaigns
The organization may incur a net loss if marketing campaigns fail to produce the anticipated outcomes. Frequently, when a business invests in advertising, it expects the resulting campaign to generate sufficient revenue to offset costs and contribute to the overall profit. Please achieve that to avoid a net loss.
3. Rising Variable Costs
Additionally, an increase in the cost of goods sold may result in a net loss. In response to an escalation in production costs, the market may demand a price increase for the product or service. If businesses incur more extraordinary variable expenses, such as those associated with basic materials and storage, they might respond by augmenting product prices, resulting in a decline in overall sales.
4. Increasing Carrying Costs
A company’s carrying costs are the expenditures associated with maintaining inventory. A business may, for instance, furnish funds for a particular form of storage, such as heating or refrigeration. Additionally, the company may pay for additional insurance for the items in storage.
Carrying costs may escalate and result in a net loss if products fail to sell at the required volume rate. No matter the cause of the change, companies incur a net loss when their income falls short of their expectations, assuming all expenses remain constant.
How To Record A Net Loss On Financial Statements?
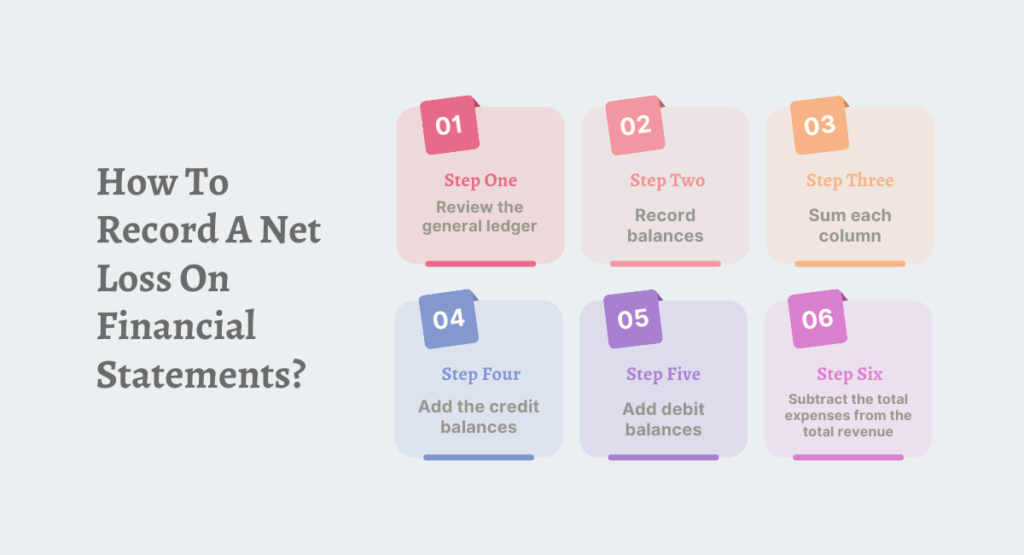
To document a net loss on quarterly or annual financial reports, adhere to the subsequent procedures:
- Review the general ledger. Accounts with a debit balance, including dividends and assets, should be identified. Then, it is possible to ascertain which accounts, including revenues and liabilities, have a credit balance.
- Record balances. Each debit balance may be recorded in the left column of a trial balance form that has been adjusted. A credit balance is recorded in the column to the right.
- Sum each column. The debit column is subsequently inserted, followed by the credit column. Investigate the ledger accounts for anomalies if the two values do not correspond.
- Add the credit balances. The total amount of revenue is calculated by adding the balances of the revenue accounts.
- Add debit balances. The company’s total expenses are equal to the sum of the balances in its expense accounts.
- Subtract the total expenses from the total revenue. If expenditures exceed revenues, the result of this computation is a negative value representing the net loss.
In Summery, The computation of net income loss is an essential component of financial analysis, as it furnishes significant insights regarding a business’s profitability and operational effectiveness. Organizations can effectively evaluate their financial performance and formulate well-informed strategic choices by adhering to these procedures and upholding stringent financial discipline. Computing net income loss is a critical competency in business and finance, regardless of one’s experience in finance or entrepreneurship.
Thank you for reading….


