A fundamental financial indicator of a company’s profitability, net income is a critical metric. It denotes the disparity that arises from including a company’s complete expenses in its revenue during a specified time frame. As an essential element of a company’s financial statements, net income is evaluated by investors, analysts, and other interested parties to assess the company’s financial health.
Although it may appear to be an impossible endeavor, the ability to calculate net income from the balance sheet is crucial for anyone interested in knowing the financial performance of a business. In this article, we will provide an overview of calculating net income from a balance sheet.
What Is A Net Income On A Balance Sheet?
As reflected on a balance sheet, net income represents the culmination of all business operations over a specified period. It is determined by subtracting the total expenses from a business’s total revenue.
The net income holds significant importance as it not only signifies the company’s profitability but also impacts retained earnings and shareholder equity, among other balance sheet components.
The Components Of A Balance Sheet
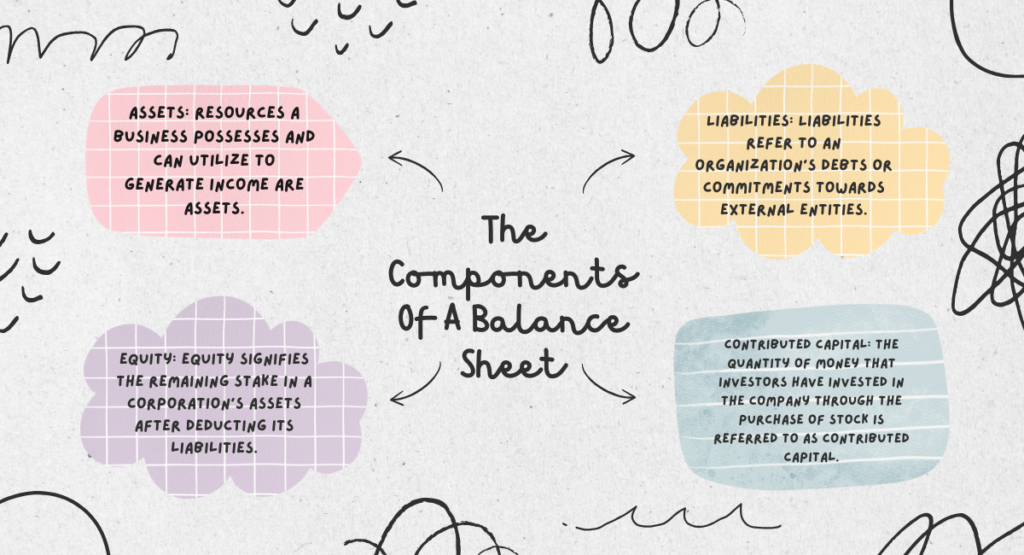
Before delving into the minutiae of calculating net income, it is essential to comprehend the balance sheet’s components. A balance sheet is a concise financial statement that presents an exact momentary depiction of the financial status of an organization. The principal components of this entity are assets, liabilities, and equity.
1. Assets: Resources a business possesses and can utilize to generate income are assets. Cash, plant, inventory, property, accounts receivable, and equipment are all examples of assets. Most of the time, assets are presented in descending order of liquidity, beginning with the most liquid assets (i.e., those readily convertible to currency).
2. Liabilities: Liabilities refer to an organization’s debts or commitments towards external entities. Liabilities comprise accounts payable, bonds, and loans, among others. Additionally, liabilities are typically arranged in maturity order, whereby the most urgent obligations—those that require payment soon—are presented initially.
3. Equity: Equity signifies the remaining stake in a corporation’s assets after deducting its liabilities. It represents the residual quantity of funds remaining after fully compensating a corporation for its obligations with its assets. Typically, two categories comprise equity: contributed capital and retained earnings.
4. Contributed Capital: The quantity of money that investors have invested in the company through the purchase of stock is referred to as contributed capital. Retained earnings are the accumulated business proceeds not distributed to shareholders as dividends.
How To Get Net Income From The Balance Sheet?
To determine net income on a balance sheet, deduct all expenses from total revenue, such as cost of goods sold, interest, operating expenses, and taxes. The resultant value constitutes the net income, a critical metric for assessing an organization’s financial well-being and profitability.
Now that we fully grasp the balance sheet’s components, we can compute net income.
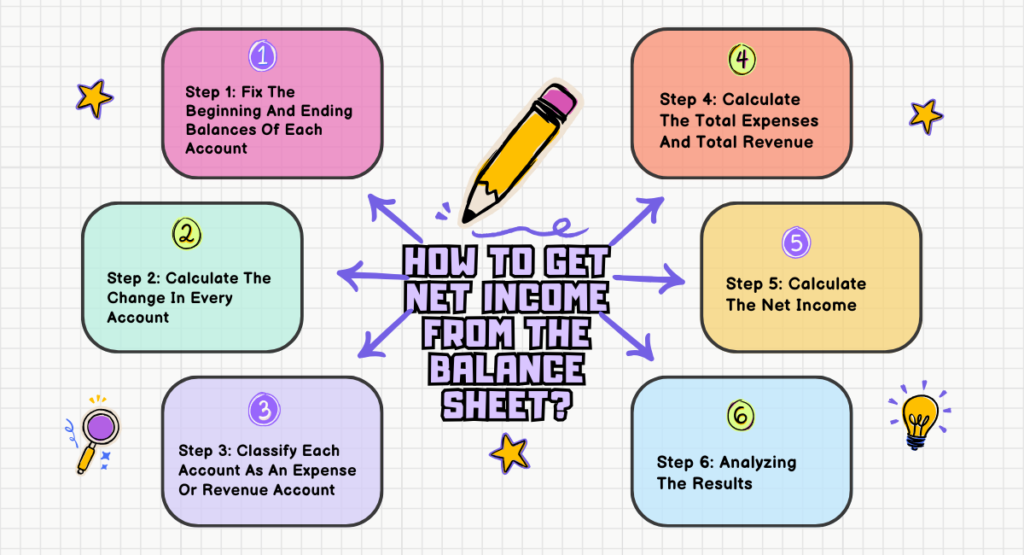
Step 1: Fix The Beginning And Ending Balances Of Each Account
To compute net income from a balance sheet, the initial stage involves ascertaining each account’s initial and final balances. Consider, for instance, the computation of a corporation’s net income for 2021. It is necessary to determine each account’s initial and final balances as of December 31, 2020, and the last day of the year 2021 on the balance sheet.
Step 2: Calculate The Change In Every Account
The next stage, following the determination of each account’s opening and closing balances, is to compute the change in each account’s balance throughout the period. To accomplish this, the beginning balance is subtracted from the ending balance.
To illustrate, in the scenario where the cash account commenced with a balance of $10,000 and concluded with a balance of $15,000, the cash account change would amount to $5,000 ($15,000 – $10,000).
Step 3: Classify Each Account As An Expense Or Revenue Account
Each account must subsequently be categorized as a revenue or expense account. Revenue accounts are financial statements that reflect the inflow of funds an organization produces, including interest income and sales revenue. Accounts that reflect expenses incurred by the business, such as rent or salaries, are called expense accounts.
Step 4: Calculate The Total Expenses And Total Revenue
After each account has been categorized as a revenue or expense account, the cumulative revenue and costs for the given period can be computed. To accomplish this, the sum of every revenue and expense account is calculated.
Step 5: Calculate The Net Income
The aggregate expenses must be deducted from the overall revenue to ascertain the net income. A net income exists when the aggregate revenue of a business exceeds the aggregate costs. A net loss is incurred when the aggregate expenses of a business exceed its entire revenue.
Step 6: Analysing The Results
It is crucial to analyze the results of the net income calculation to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the company’s financial performance. One approach to accomplish this is by conducting a comparative net income analysis with preceding periods. This information may indicate whether the company’s profitability is increasing or decreasing as time passes.
Additionally, the results can be evaluated by comparing the net income to that of other firms in the same industry. This can provide valuable insights regarding the company’s performance compared to its industry counterparts and whether it is experiencing superior or inferior growth.
Importance Of Net Income On A Balance Sheet
A balance sheet’s net income is an essential indicator of the profitability of a business. It explicitly assesses a company’s financial achievement by showcasing the extent to which revenue surpasses expenses.
Net income emerges as a pivotal metric that impacts investment decisions for stakeholders and investors. It provides valuable insights into the company’s management effectiveness and its prospects for future expansion.
Presentation Of Net Income On A Balance Sheet
Net income is disclosed in the equity section on a balance sheet, more precisely as a constituent of retained earnings. A balance sheet comprises three fundamental components: assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
Earnings under shareholders’ equity are increased by transferring net income from the income sheet to the balance sheet. Effectively, net income signifies the augmentation of an organization’s financial resources during a designated time frame.
Analysis And Interpretation Of Net Income
A balance sheet analysis of net income provides a wealth of information regarding the financial well-being of a business. The value above is crucial when calculating profitability ratios, including the net profit margin, which indicates the company’s efficiency in converting revenue into profit.
An additional critical element is the regularity of income, which determines the character of earnings. In addition, net income is interconnected with several other financial indicators, which impact calculations, such as return on equity and earnings per share.
In Summary, Although the process of deriving net income from a balance sheet may initially appear complex, mastering this ability is vital for anyone seeking to comprehend the financial performance of a business. By performing the procedures delineated in this article, one can ascertain the net income of a corporation and acquire significant knowledge regarding its profitability.
Remember to compare the net income to prior periods and other firms in the same industry to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the company’s financial health through analysis of the results.
Thank you for reading….
Read more: How To Find The Book Value Of Equity?


